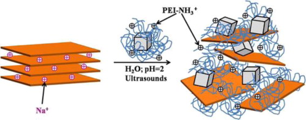
Hybrid materials formed by the combination of a sodium rich Montmorillonite (MMT), with magnetite nanoparticles (40 nm, Fe3O4 NPs) coated with Polyethylenimine polymer (PEI 800 g/mol or PEI 25000 g/mol) were prepared. The intercalation of the magnetite nanoparticles coated with PEI among MMT platelets was achieved by cationic exchange. The resulting materials presented a high degree of exfoliation of the MMT sheets and a good dispersion of Fe3O4 NPs on both the surface and among the layers of MMT. The presence of amine groups in the PEI structure not only aids the exfoliation of the MMT layers, but also gives to the hybrid material the necessary functionality to interact with heavy metals. These hybrid materials were used as magnetic sorbent for the removal of hexavalent chromium from water. The effect that pH, Cr(VI) concentration, and adsorbent material composition have on the Cr(VI) removal efficiency was studied. A complete characterization of the materials was performed. The hybrid materials showed a slight dependence of the removal efficiency with the pH in a wide range (1–9). A maximum amount of adsorption capacity of 8.8 mg/g was determined by the Langmuir isotherm. Results show that these hybrid materials can be considered as potential magnetic adsorbent for the Cr(VI) removal from water in a wide range of pH.