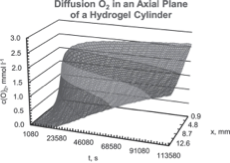
Polymer network membranes with a high capacity for water absorption are obtained by radical polymerization of N-[2-(2-hydroxyethoxy)ethyl]methacrylamide (HEEMAM). The permeability, solubility, and diffusion coefficients of oxygen in hydrogels are determined using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) methods based on the paramagnetic effect of dissolved oxygen gas on the proton spin-lattice relaxation times of water, and the results are compared with those obtained with electrochemical procedures. The results of NMR measurements of oxygen transport coefficients in distilled water show excellent agreement with corresponding literature values. The results of the potentiostatic and NMR oxygen transport measurements in hydrogels are in reasonable agreement and support the viability of the NMR method. An NMR method to determine the transport coefficients of oxygen in hydrogels is proposed. The method exploits the paramagnetic properties of the oxygen gas and its effect on the water proton NMR spin-lattice relaxation time to map the spatial and temporal concentrations of dissolved oxygen in hydrated gels