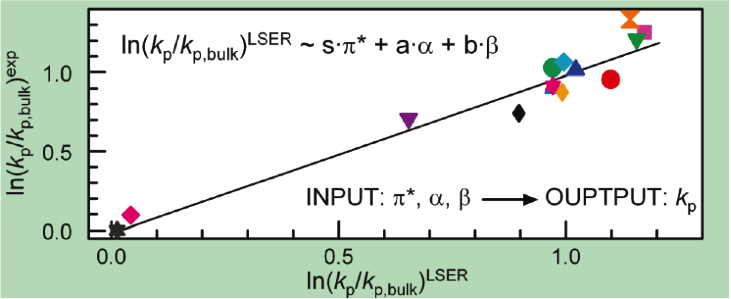
Pulsed laser initiated polymerizations of methyl methacrylate (MMA) in the presence of ionic liquids (ILs) resulted in a strong enhancement of the propagation rate coefficient, kp, compared to the bulk system. To correlate the IL influence on MMA kp with IL solvent properties, the Kamlet-Taft parameters a, ß, and p? of the ILs were derived. A correlation in the form of ln(kp/kP,bulk)= ln(k p/kp,bulk)0-spF-aa+bß was obtained from a linear solvation energy relationship (LSER) analysis of a data set consisting of polymerizations in 11 ILs, as well as in DMSO, in THF, and in bulk. The coefficients are s = 1.72, a = 0.63, b = 0.37, and ln(k p/kP,bulk)0 = -1.27. The data indicate that dipolarity, polarizability, and electron pair accepting ability of the IL, associated with the p* parameter, contribute to a large extent to the variation in kp, whereas electron pair donating and hydrogen bond accepting ability, accounted for by ß, are of lesser importance. The hydrogen bond donating ability, related to a, of the IL has no significant influence on kp